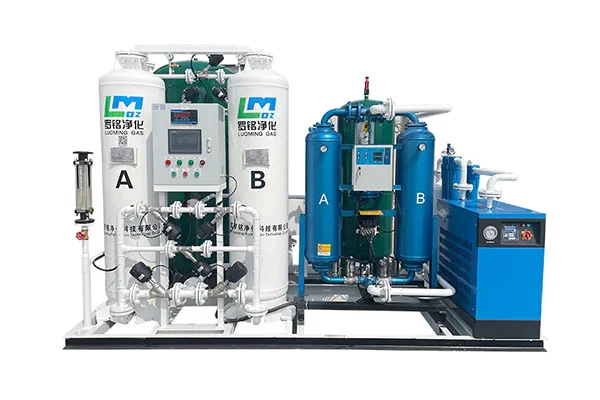
PSA Nitrogen Generation System
Custom-Built PSA Nitrogen Generator
- High nitrogen purity with maximum purity up to 99.9995%
- Rapid startup with qualified nitrogen available within 30 minutes
- Online monitoring and display of nitrogen purity, flow rate, and pressure
- Fully automatic control supporting unattended operation
- Skid-mounted integrated structure with compact footprint and easy installation
- Customized pressure and dew point configurations, dew point down to -70°C available
- Nitrogen capacity: 1-3000Nm³/h (standard conditions)
- Nitrogen purity: 95%-99.9995%
- Outlet pressure: 0-0.65MPa (adjustable), other pressure ranges available on request
- Atmospheric dew point: ≤-40°C (standard), optional down to -70°C
Selective adsorption of carbon molecular sieve combined with pressure swing operation
The fundamental principle of the nitrogen generator lies in adsorption differences between oxygen and nitrogen on carbon molecular sieve. Pressurization enables selective adsorption, while depressurization releases adsorbed components and restores adsorption capacity.
Differential Adsorption
- The microporous structure of carbon molecular sieve exhibits significantly higher adsorption affinity for oxygen than for nitrogen. Due to kinetic effect, oxygen molecules diffuse through sieve micropores at a rate approximately three to five times faster than nitrogen molecules. Under elevated pressure, adsorption capacity increases further, enhancing separation efficiency.
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) cycle
- During pressurization, carbon molecular sieve preferentially adsorbs oxygen, carbon dioxide, and moisture, allowing nitrogen to enrich in the gas phase. During depressurization, previously adsorbed impurities are released, restoring adsorption performance. Alternating operation of dual adsorption towers ensures uninterrupted nitrogen output.
Five-step process converts ambient air into high-purity nitrogen.
Feed air pretreatment ensures adsorption efficiency.
- Using ambient air as feedstock, the air first passes through a multi-stage filtration system (comprising primary, fine, and activated carbon filters) to remove impurities such as dust (≥0.1μm), oil mist (≤0.1mg/m³), and moisture (dew point ≤-40℃)
- Purified air enters an oil-free air compressor and is compressed to 0.6-0.8MPa, providing the required pressure for adsorption.
- Compressed air then passes through refrigerated dryers and absorption dryers to further reduce dew point, typically to ≤-40°C, with optional configurations reaching -70°C, preventing moisture damage to molecular sieve.
Nitrogen and oxygen separation occurs through alternating adsorption towers.
Purified compressed air enters dual adsorption towers controlled by a PLC-based valve switching sequence. Continuous adsorption and regeneration cycles maintain stable nitrogen output.
- During adsorption, compressed air enters Adsorption Tower A at 0.6-0.8MPa. Carbon molecular sieve rapidly adsorbs oxygen, carbon dioxide, and moisture, while nitrogen exits from the top of the tower as product gas with purity of 95%-99.9% for standard configurations.
- Simultaneously, Adsorption Tower B undergoes depressurization to atmospheric pressure. Adsorbed impurities are released from the bottom of the tower, restoring adsorption capacity. Selected configurations introduce a small portion of product nitrogen for purge regeneration, improving desorption efficiency.
- Tower switching occurs every 30-120 seconds under PLC control, ensuring continuous nitrogen supply without interruption.
Optional nitrogen purification supports ultra-high purity requirements.
For applications requiring nitrogen purity of 99.5%-99.9995%, additional purification stages are integrated.
- Hydrogen-Based Purification: Utilizing the reaction 2O₂ + 2H₂ → 2H₂O, residual oxygen reacts to form water mediated by a catalyst (nickel catalyst). Generated moisture is removed by drying units, producing nitrogen purity ≥99.999%, suitable for flow rates up to 500Nm³/h.
- Carbon-Based Purification: Utilizing the reaction O₂ + C → CO₂ (or CO), carbon-based purification removes residual oxygen through reaction with carbon-based adsorbents, followed by carbon dioxide removal. Nitrogen purity reaches up to 99.999% without hydrogen introduction, supporting applications sensitive to hydrogen, including electronics manufacturing.
Pressure regulation and storage ensure stable nitrogen output.
- Produced nitrogen enters a buffer tank, where pressure is stabilized at 0.1-0.65MPa through pressure regulating valves, preventing pressure fluctuation from affecting downstream applications such as laser cutting and food packaging.
- Selected configurations integrate nitrogen storage tanks to store nitrogen during low-demand periods and release nitrogen during peak consumption, supporting intermittent nitrogen demand in chemical processing and similar applications.
Nitrogen delivery and monitoring enable real-time purity control.
- Stabilized nitrogen is delivered to terminals through pipelines, including welding stations, packaging machines, and GC/LC units.
- Online monitoring instruments including oxygen analyzers, dew point meters, and flow meters display nitrogen purity from 95% to 99.9995%, flow rate, and pressure in real time. Audible and visual alarms activate when purity deviates from set limits.
| Model | Purity | Nitrogen capacity (Nm³/h) | Inlet nominal diameter | Outlet nominal diameter |
| 99% | 1 | DN15 | DN15 | |
| 99% | 5 | DN15 | DN15 | |
| 99% | 10 | DN15 | DN15 | |
| 99% | 20 | DN20 | DN15 | |
| 99% | 30 | DN20 | DN25 | |
| 99% | 40 | DN20 | DN25 | |
| 99% | 50 | DN32 | DN25 | |
| 99% | 100 | DN32 | DN40 | |
| 99% | 120 | DN40 | DN40 | |
| 99% | 150 | DN40 | DN40 | |
| 99% | 200 | DN50 | DN40 | |
| 99% | 500 | DN80 | DN40 | |
| 99% | 800 | DN100 | DN80 | |
| 99% | 1000 | DN100 | DN100 | |
| 99% | 2000 | DN125 | DN100 | |
| 99% | 3000 | DN125 | DN125 |